Connect to your Active-Active databases
With the Redis database created, you are ready to connect to your database to store data. You can use one of the following ways to test connectivity to your database:
- Connect with redis-cli, the built-in command-line tool
- Connect with a Hello World application written in Python
Remember we have two member Active-Active databases that are available for connections and concurrent reads and writes. The member Active-Active databases are using bi-directional replication to for the global Active-Active database.
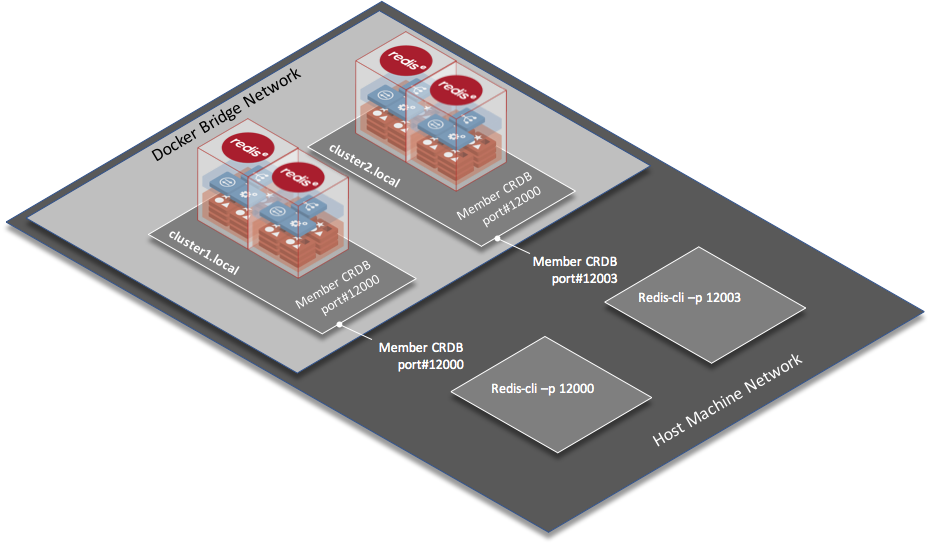
Connecting using redis-cli
redis-cli is a simple command-line tool to interact with redis database.
To use redis-cli on port 12000 from the node 1 terminal, run:
redis-cli -p 12000Store and retrieve a key in the database to test the connection with these commands:
set key1 123get key1
The output of the command looks like this:
127.0.0.1:12000> set key1 123 OK 127.0.0.1:12000> get key1 "123"Enter the terminal of node 1 in cluster 2, run the redis-cli, and retrieve key1.
The output of the commands looks like this:
$ redis-cli -p 12000 127.0.0.1:12000> get key1 "123"
Connecting using Hello World application in Python
A simple python application running on the host machine can also connect to the database.
In the command-line terminal, create a new file called “redis_test.py”
vi redis_test.pyPaste this code into the “redis_test.py” file.
This application stores a value in key1 in cluster 1, gets that value from key1 in cluster 1, and gets the value from key1 in cluster 2.
import redis rp1 = redis.StrictRedis(host='localhost', port=12000, db=0) rp2 = redis.StrictRedis(host='localhost', port=12002, db=0) print ("set key1 123 in cluster 1") print (rp1.set('key1', '123')) print ("get key1 cluster 1") print (rp1.get('key1')) print ("get key1 from cluster 2") print (rp2.get('key1'))To run the “redis_test.py” application, run:
python redis_test.pyIf the connection is successful, the output of the application looks like:
set key1 123 in cluster 1 True get key1 cluster 1 "123" get key1 from cluster 2 "123"